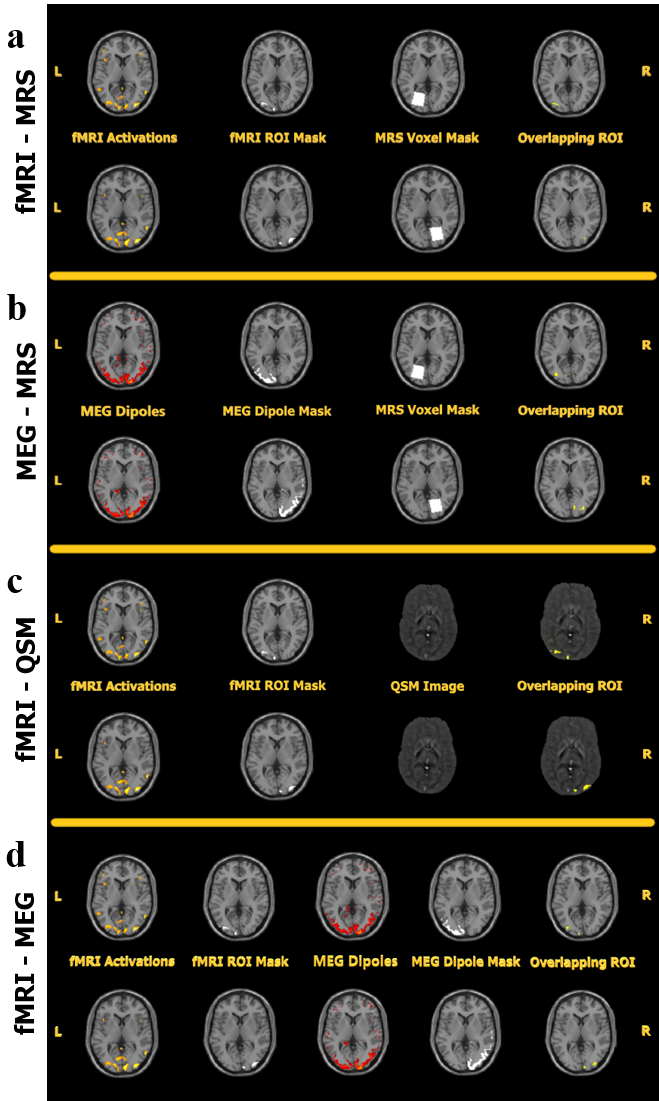
Figure 1: Representative results of unimodal data processing and intermediate steps of bimodal data integration. In each section, the first row represents LOC and the second row represents ROC. a. fMRI-MRS Integration shows the fMRI activations (checkerboard paradigm), corresponding activation mask for the respective ROI, and normalized MRS voxel mask, followed by the resulting overlapping region. b. MEG-MRS Integration represents the MEG dipoles (checkerboard paradigm), corresponding dipole mask, and the normalized MRS voxel mask for the respective ROIs followed by the resulting common region. c. fMRI-QSM Integration fMRI activations, corresponding activation mask for the respective ROIs, QSM image of the same brain slice, followed by the resulting overlapping region are shown. d. fMRI-MEG Integration shows the fMRI activations, corresponding mask for the respective ROI, MEG dipoles, and dipole mask for respective ROIs, followed by the resulting overlapping region.
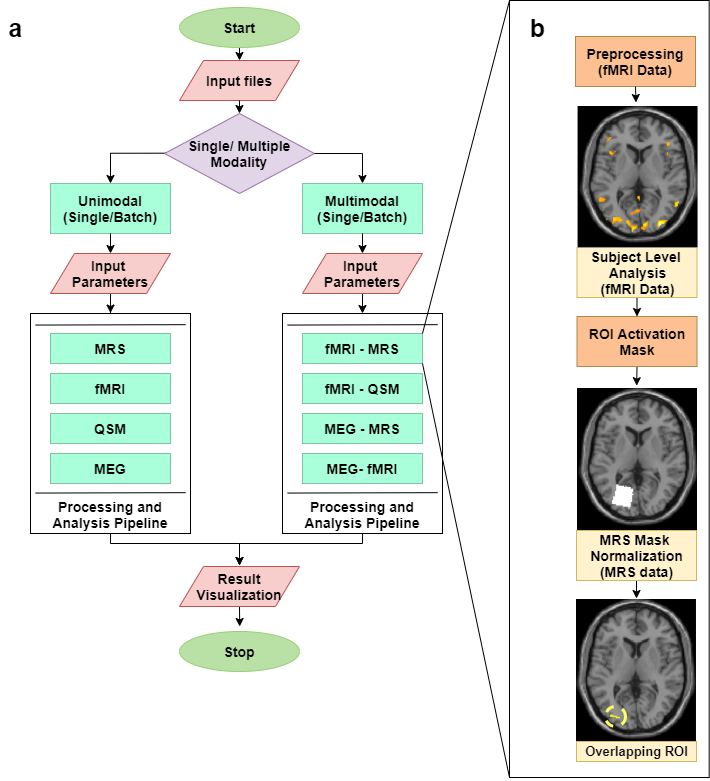
Figure 2: Multimodal Data Integration (MDI) Toolbox Execution Scheme: a. The pipeline begins with the input of data files and choosing between single and multimodal data processing, followed by the execution of the respective processing steps and visualization of the resulting common region. b. Data processing and integration pipeline for the fMRI-MRS combination has been shown inset. This pipeline involves pre-processing of the fMRI data followed by single level analysis and creation of an ROI activation mask. This is followed by the generation of normalized MRS voxel masks. These masks are spatially integrated to get an isolated common region.